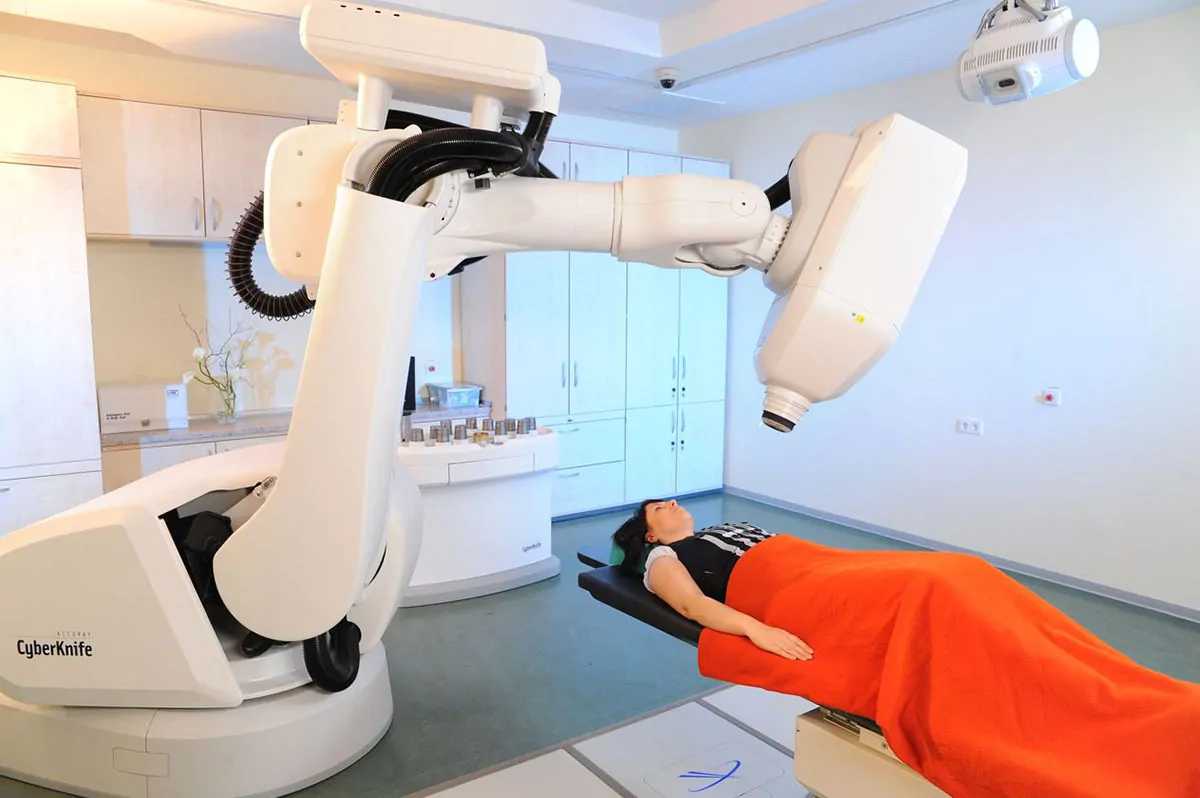
Robot-assisted CyberKnife
CyberKnife stands for one of the most advanced therapies for treating many tumor types by assuring the highest level of comfort for the patient. As a result of the sophisticated digital image guidance and robotic control, high radiation doses can be focused with an accuracy of fractions of a millimetre. This guarantees a minimum effect on healthy organs at maximum effectiveness. As the only system worldwide, CyberKnife is able to balance the respiration-induced movements in the body. This is of decisive advantage, particularly for moving tumors in the lungs and liver. Our team and partners have been working on the development of the CyberKnife for years. Thus, our expertise is unique worldwide and our treatment results speak for themselves.
Innovative Developments from Germany
Since the dawn of robotic radiosurgery, the Institute for Robotics and Cognitive Systems at the University of Lübeck has been playing an important role in the innovative CyberKnife development, based on the latest soft- and hardware technologies. Key areas include robot control, treatment planning and prediction, and compensation of movements. Many CyberKnife components have been developed by our team and partners in Germany:
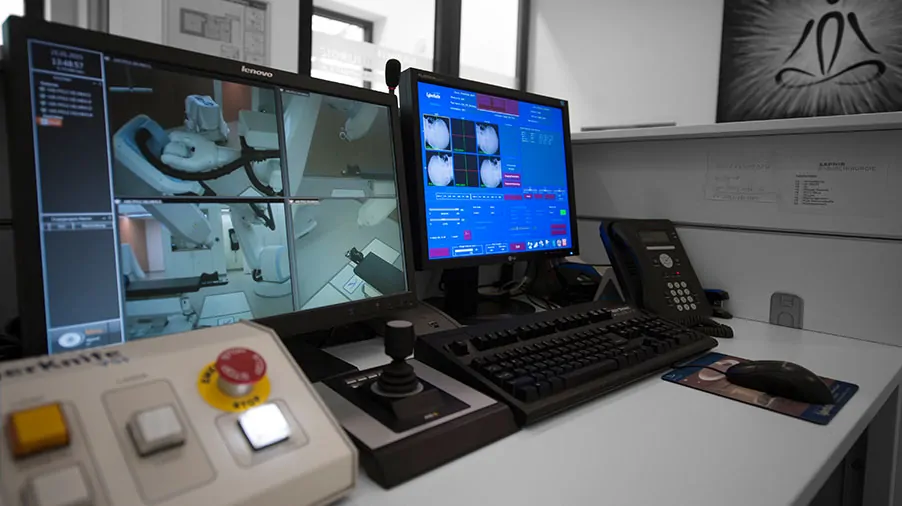
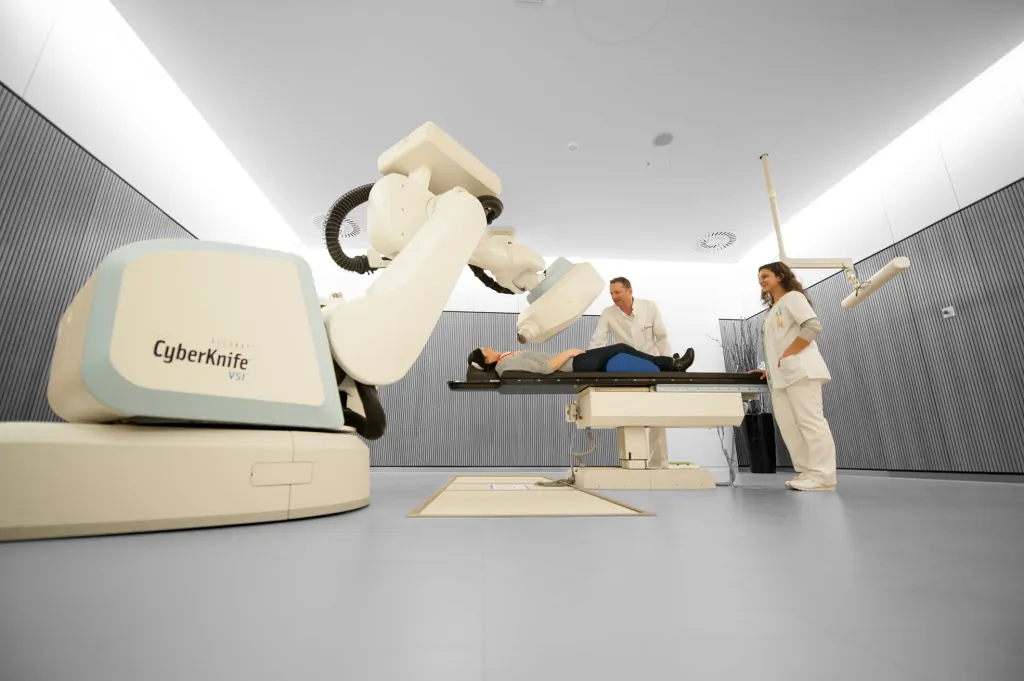

Technology and Physics
The CyberKnife is excellently suited for intracranial radiosurgery, that is to say for treatments within the skull. This technology is superior to any conventional system – documented in numerous technical and clinical studies. Even with moving tumors (e.g. in the lungs and liver) the CyberKnife System represents the most accurate treatment system with a minimum of uncertainty.
The SAPHIR team works closely together with the Institute of Robotics and other leading centers for medical physics. In this respect our radio surgery centers are among the most technically experienced treatment centers worldwide. Furthermore, we are setting new standards of quality assurance and irradiation planning – a great benefit for our patients. Our research and development programme also includes innovations such as the ultrasound or MRI-guided radiosurgery or heart radiosurgery.